What is CAD?
CAD simply stands for Computer-aided design. It is the application of computer technology in designing products and documents the process of the design. CAD is also sometimes referred to as Computer-aided design and drafting (CADD). Whether CAD or CADD it is a technology for technical documentation and designs.
This technology abruptly stops the use of manual drafting and introduces an automated process. Somehow, you may have used this technology without even realizing it. If you have used AutoCAD or any other 2D or 3D CAD programs, then you have experienced this technology. It produces both two-dimensional and three-dimensional diagrams with proper details and specifications.
Most times, CAD outputs require a plotter or special printer for professional design printing. CAD utilizes a workstation that aids in the whole process such as the creation, analysis, and modification of designs. The applicability of CAD cuts across many industries and fields. For instance, in mechanical design, it is best referred to as Mechanical Design Automation (MDA), although it is often called computer-aided drafting (CAD). In electronic systems are referred to as Electronic Design Automation (EDA). Before we dive deep into the CAD let’s look at the history of CAD.
History of CAD
CAD dates far back to the ‘60s with the IBM Drafting Systems. It was initially developed to reproduce manual drafting. Companies began switching to CAD once they discovered the cost-benefit. The ability to perform engineering calculations was integrated into CAD and this encouraged the use by engineers. Although calculations by hands were still done by some, CAD spread would not be hampered.
CAD brought a revolution which merged roles of designers, draftsmen, and engineer in the engineering industry. Initially, CAD was mainly for 2D and 3D engineering drawings. Gradually it transcended beyond that and became the bedrock of all engineering drawing. Today CAD is used virtually in all engineering design processes right from the idea conceptualization, product designs, product layouts, to assembly analysis. The use of CAD goes as far as jewelry, appliances, and furniture. Recent improvements have seen CAD finds its use in animations and advanced rendering for optimized visualization. A typical example is 4D BIM which offers a virtual construction simulation for project management. CAD today enables designers and engineers to create designs and objects with ease and have options for saving, printing, exporting, and editing.
The days without CAD
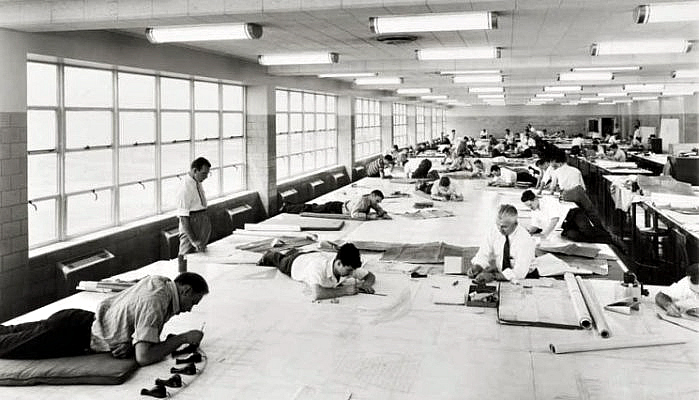

The era without CAD has fizzled out unnoticed. The evolution of CAD automated the manual pencil and ruler draw. Before CAD, draftsmen and engineers make designs, using traditional tools such as pencils, rulers, drafting board, drafting machine, T-square, French curves, compass, and drafting papers. Reproducing the drawing was a herculean task even with the introduction of large format photocopiers. The history of manual drawing dates to the ancient Egyptians. Making a design took several hours of measuring, ruling, and drawing.
Leading CAD Software nowadays
Due to popular demands, several developers came up with plenty of CAD software offering a wide range of flexibility in designs. The result of all the software may be the same but the user interfaces, tools, and flexibility may differ. Designers and engineers often use one or a combination of two or three to complete design projects depending on what the design entails. Here are some of the best CAD software available today in no order.
Solidworks
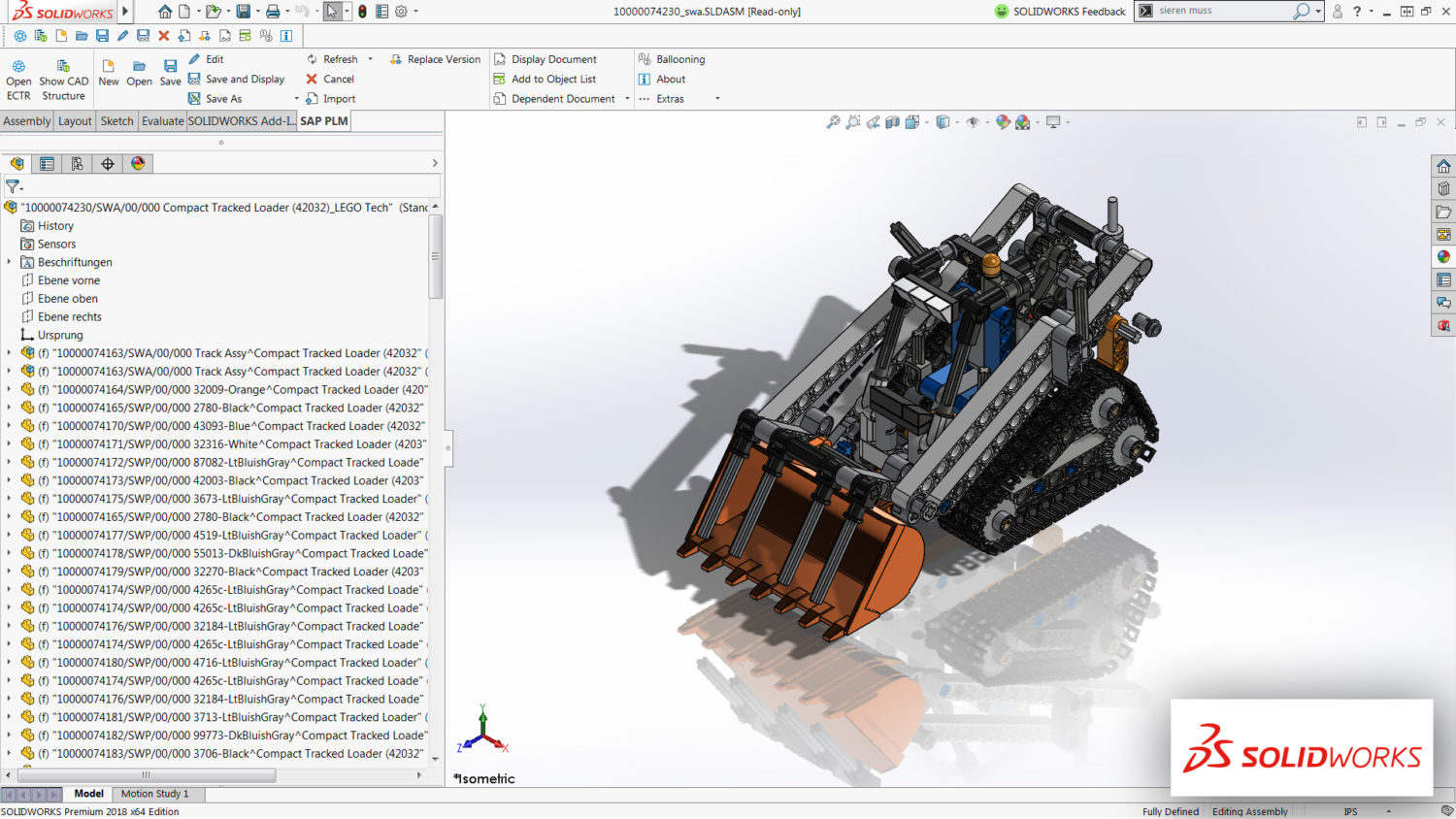
Professional 3D designers often use this software for 3D designs. It’s quite popular amongst engineering students in the universities. Dassault Systèmes published this software on November 1, 1995. This parametric feature-based software offers a wide range of design validation tools which is useful for reverse engineering. Solidworks is super ideal for creating industrial objects since it’s very detailed and practical. It uses NURBS systems for curves that stand out from the regular flat structure inclination in other software. You can create curvatures with good details with the software. It also utilizes dimensional sketching instead of polygon modeling. One major setback of Solidworks the limitation on importing (.STL extension) files. You would require another program to be able to edit the.STL files. All in all, it is recommendable CAD software.
CATIA
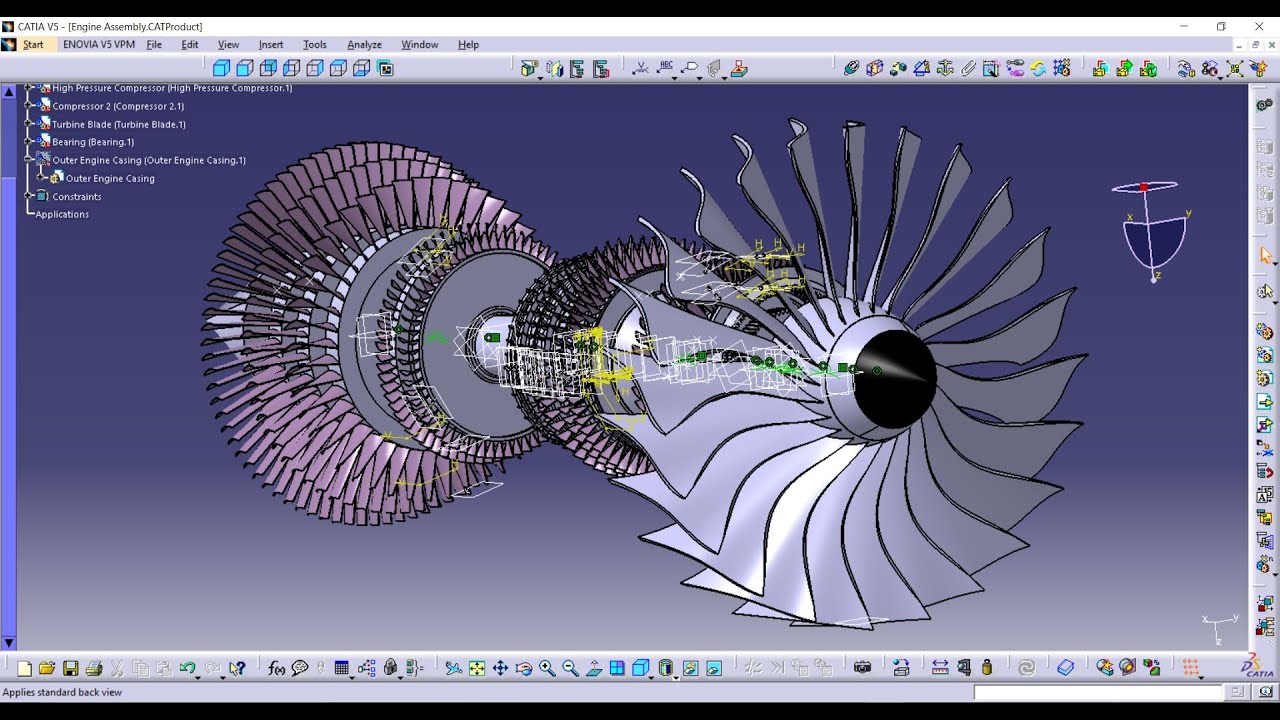
This is arguably one of the simplest CAD software available today. This software originally developed for the needs of Dassault Aviation offers both CAD, Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM), and Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE). This software integrates various approaches to product designing and development. It offers designers several tools for design optimization. It applies to building and industrial designs.
Siemens NX
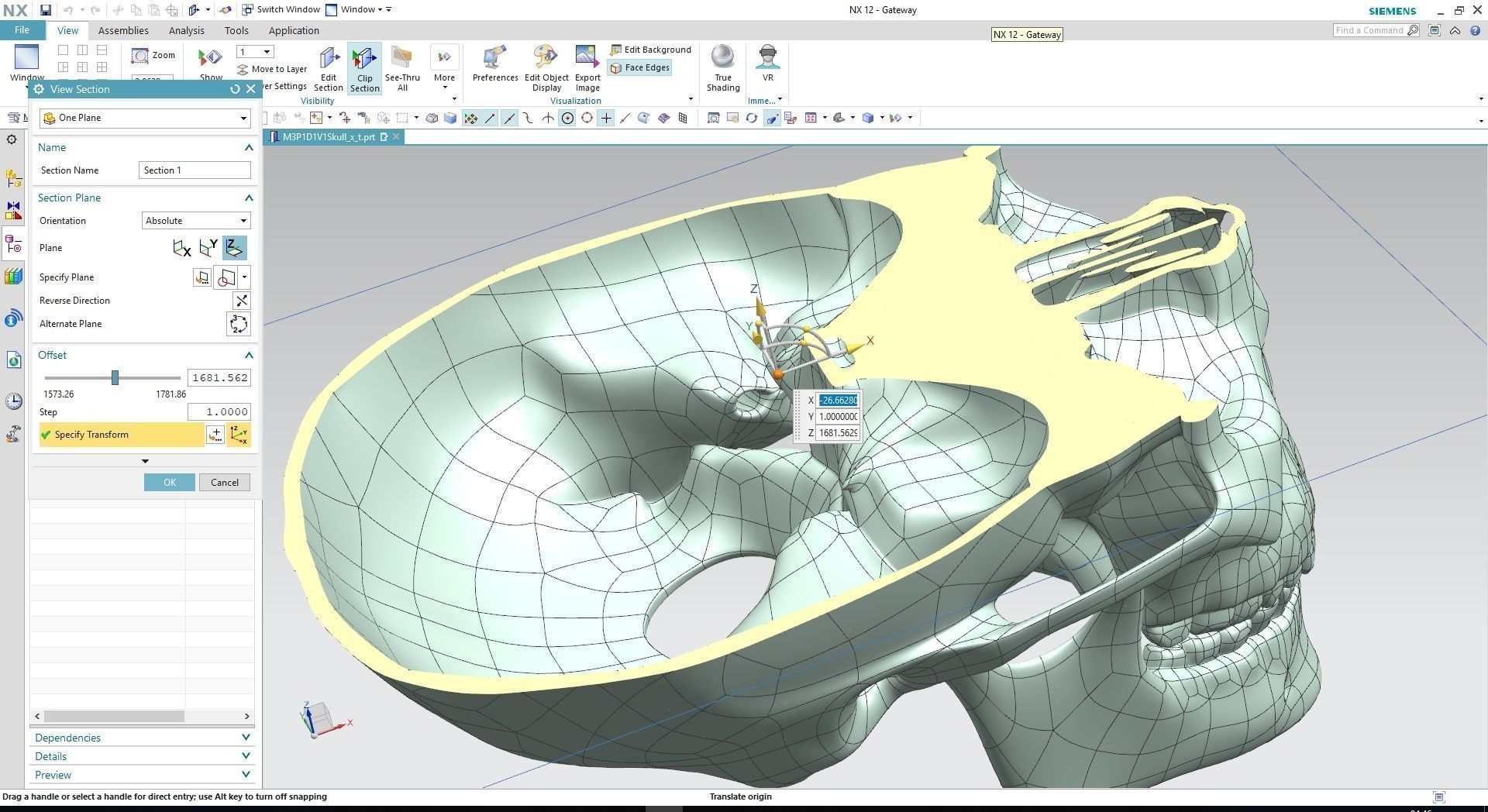
Developed by Siemens PLM Software, Siemens NX is an advanced and powerful software with flexible tools for easy simulations and design developments. Formerly known as Unigraphics, this CAD software enable efficient and faster design delivery. NX allows designers to create the next generation of simulations and designs. It’s a super combo that can easily integrate with other CAD software. With NX you can achieve the best of CAD, CAM, and CAE designs.
AutoCAD
This is the most popular and the first CAD software available in the market since 1982. Autodesk developed this CAD software to enable the designer to make 3D designs easily. It is so popular that fully functional versions are readily available for schools and students. It is mostly ideal for 2D but not has 3D capabilities for anyone with excellent designing skills. AutoCAD 360, the web-app version is also available.
Creo
Creo CAD software is developed by Parametric Technology Corporation. It offers many functionalities such as motion, structural, freestyle, and thermal. It is a complete tool for modeling ideas into designs. It is ideal for manufacturing industries. It is been in the CAD software market for over 30 years. Trial versions are also available.
Revit
Revit CAD software from Autodesk offers sophisticated tools for optimizing designs. It is ideal for creating real-world structures. It is most applicable for Building information modeling (BIM) where architects apply the tools to create near real-life designs. It produces quality building designs.
FreeCAD
This is one kind of completely free 3D software. This parametric-based software has modeling tools that enable users to create near the real-life design of different sizes. It has a superb zooming feature. Different tools are available for different purposes. FreeCAD is more suitable for training and not for professional designs. It is a good tool for any beginner.
Fusion 360°
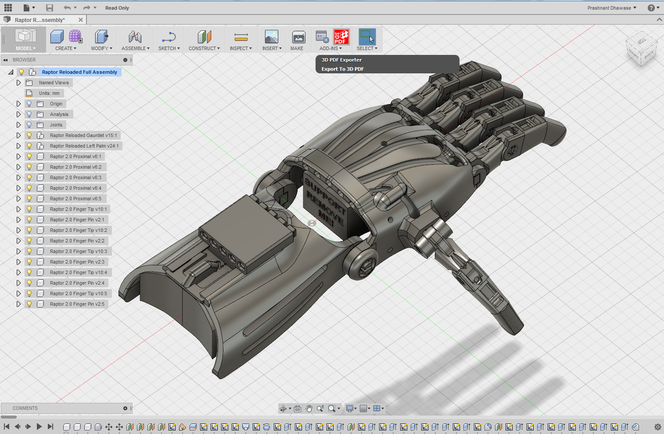
This is a unique cloud-based 3D CAD tool that utilizes the cloud to match users together to complete designs together from different locations. Although professionals pay monthly to use this cloud-based software, it available for students and academic instructions for free. One of the major advantages is the ability to save the entire history of the designs. Users can retrace the steps backward for learning purposes. Mesh modeling, solid modeling, and freeform are some of the design options it offers.
Rhino
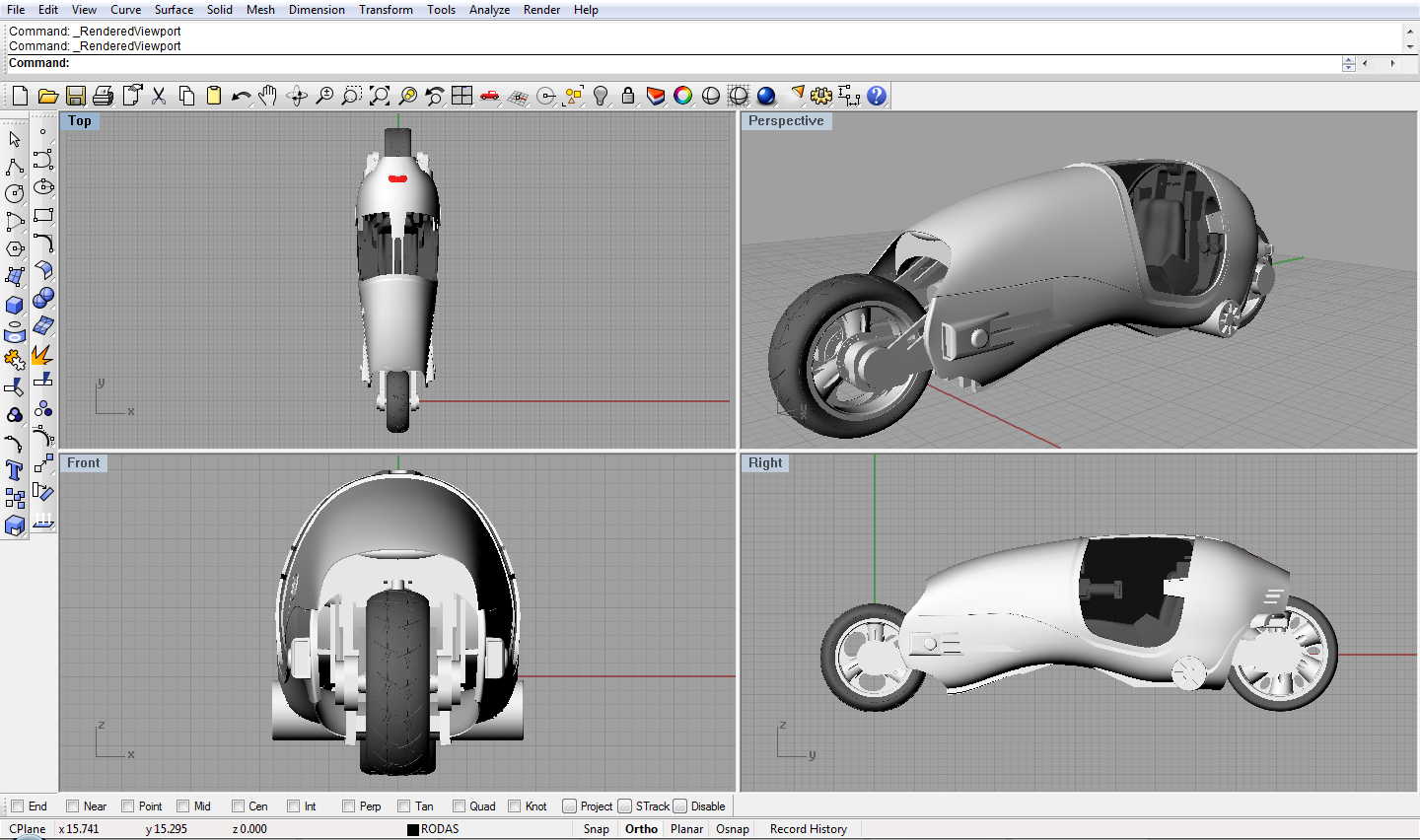
This software uses NURB which enables its multiple functionalities. It allows prices and accurate manipulation of points, meshes, curves, and solids. It arguably one of the best commercially available 3D software available in the market. It is also useful for computer graphics. Rhino offers a wide range of features that enables complex designing. It is said to be one of the most difficult CAD software to learn because of its several tools.
Inventor
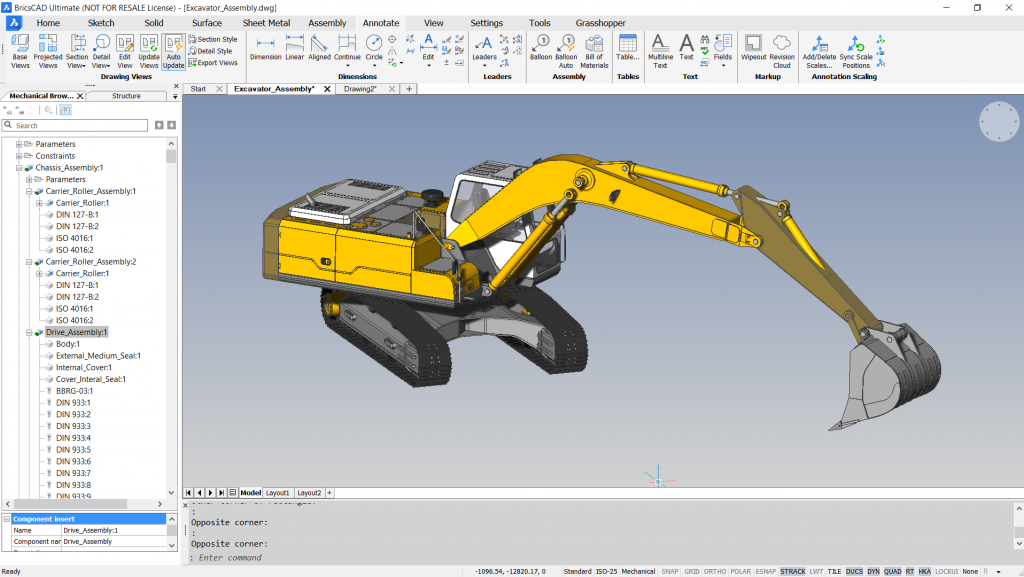
Autodesk Inventor offers a variety of tools for 3D designs, simulations, and visualization. It is parametric-based which serves for mechanical drawings. Industries like architects, construction, and automotive find it very useful. It was developed by John Walker in 1982 alongside 12 partners.
Others worthy of mentions include OpenSCAD, BlocksCAD, and TinkerCAD
The benefit of using CAD
CAD offers numerous benefits besides time saving and improved quality. Here are a few benefits of using CAD.
Better Quality Designs
CAD transformed the quality of designs starting from idea visualization to the final product design. CAD gives engineers the ability to control the quality of the products by optimizing the designing tools. Different versions of the final products can easily be seen before even making a prototype. This saves time and cost.
Increase in Productivity
The use of CAD software drastically lowers production costs since engineers can now work faster and smarter. It saves time which reduces project completion time. It allows manufacturers to produce at a reduced cost, good quality, and faster also. CAD gives the company a competitive edge in the global market place. It allows companies to visualize products during conception before launching.
Compatibility
CAD makes designs easier to read. They are several applications available for reading and editing CAD design file no matter the format. Paper and pencil drawing could be unclear or damaged in the transit, but CAD designs survive all this. 3D modeling makes it very easy for even a novice to read and understand drawings. CAD makes file sharing almost seamless. One design can travel faster and longer than a human.
Documentation
Most CAD software can document all aspects of the design. It can store the record of angles, measurements, dimensions as well as other parameters. You can save it for future reference at no cost. Also, this CAD enables easy generation of Bill of Materials (BOM). The applicability of CAD for mechanical engineers in design documentation is very vital.
Flexibility of designs
With CAD, engineers can easily reuse and change designs, something paper drawing couldn’t offer. In the fashion design industry, for instance, a designer can tweak drawing several ways to get different models without starting a fresh drawing. The main design files can be used several in the manufacturing process which saves cost and time.
3D Printing
This process creates a three-dimensional output from a finished CAD design by building on multilayer material. Materials are added layer by layer in a three-dimensional manner. One major advantage of 3D printing is that extreme complex geometries such as internal hollow or truss can be achieved. It was mostly applicable to prototypes because of its detailed nature. CAD software can produce a digital 3D file that a 3D printer can print interpret.
Future of CAD
The integration of the cloud into CAD is shaping the future of designs. Cloud brings an additional advantage of collaborating with other engineers irrespective of the geological locations. Different stages of designs can be split into several engineers which brings a collation of ideas.
Also, the ability to customize design software to suit a purpose is the next game-changer. When this happens, industries can have specialized CAD software only suitable for their need. Software tailored to meet the requirement of an industry rather than a generic and multipurpose platform available.
Contribution of CAD in the revolution of Industry 4.0
Smart Industries will integrate the multidimensional benefits of CAD. The automation and seamless operation of industries will also include the design processes. Robots and AI can be incorporated to use CAD software embedded in its programming to create innovative designs. This will make a manufacturing process compact, autonomous, and mostly independent.