Blow molding technology is the most popular method used to produce hollow or double-wall products out of thermoplastic material. Blow molding evolved from the ancient method of glass blowing. Today it is a leading plastic manufacturing process, because of the wide range of plastic resins that can be blow-molded and the many variations in the molding process.
In this article, we’re going to explore this technology in detail and understand the history of how this technology became the leading manufacturing process in the world.
What is blow molding?
Blow molding is a manufacturing process in which hollow containers are formed by heating thermoplastic material to its melting point. It’s a very different process from Injection molding. There are many variations of the process, but the basic process is the same for all of them.
The basic process can be divided into three parts- Melting, Plastic Formation, Blowing and Molding
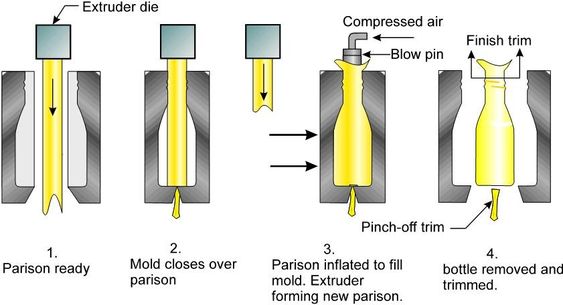
1. Melting into parison
The thermoplastic material being used is heated until it reaches its melting point. The material is melted so that it’s possible to reshape it easily. At the melting point, the material is made to form a hollow tube called a parison or preform.
2. Plastic formation
The parison or preform of the heated material is then placed between two identical female molds. The molds close and clamp around the parison or preform, giving the tube a primary shape of the desired container.
3. Blowing and Molding
Then pressurized is blasted through the open end of the tube which forces the parison or preform to take the shape of the closed mold. This is the desired final shape of a container or a bottle. The material is then allowed to cool and the female molds are separated from the hollow part. The container then goes through a trimming process that smoothens the outer layer of it.
History and Development of Blow Molding
To properly understand and appreciate a technology, we must know the history behind its development. Knowing the history is also important because that makes us appreciate the amazing human efforts that are responsible for its development.
The Syrians used air to blow hot material for the first time long before the birth of Christ. They used a tube to blow into the hot material with their mouth. This process went on for a thousand years before it was refined in Europe by the English. The people of England developed a system that included blowing the hot blob of glass into a mold to produce these bottles.
If we fast forward another thousand years, we see our current world which has gone through an industrial revolution. The modern era of blow molding technology began in 1938 by the production of a machine by Enoch Ferngren and William Kopitke. That was the beginning of a commercial blow molding process worldwide.
The worldwide success of this technology was due to the enormous demand for plastic and plastic-based products.
Types of Blow Molding
Depending on the machinery used and the manufacturing process, there are three main variations of the blow molding technology-
1. Injection Blow Molding
Injection blow molding is used primarily for the production of small pharmaceutical or personal product containers. This process is better than extrusion blow molding for making small products that require high production volume. No plastic waste or trim is generated with the lastest IBM machines, except for improperly formed containers.
The process starts by producing a molded parison called a preform by injecting a thermoplastic material into a cavity and around a core rod. The preform is then transferred to the blow mold which is clamped around it. Then pressurized air is blown into the preform for the shaping of the final form.
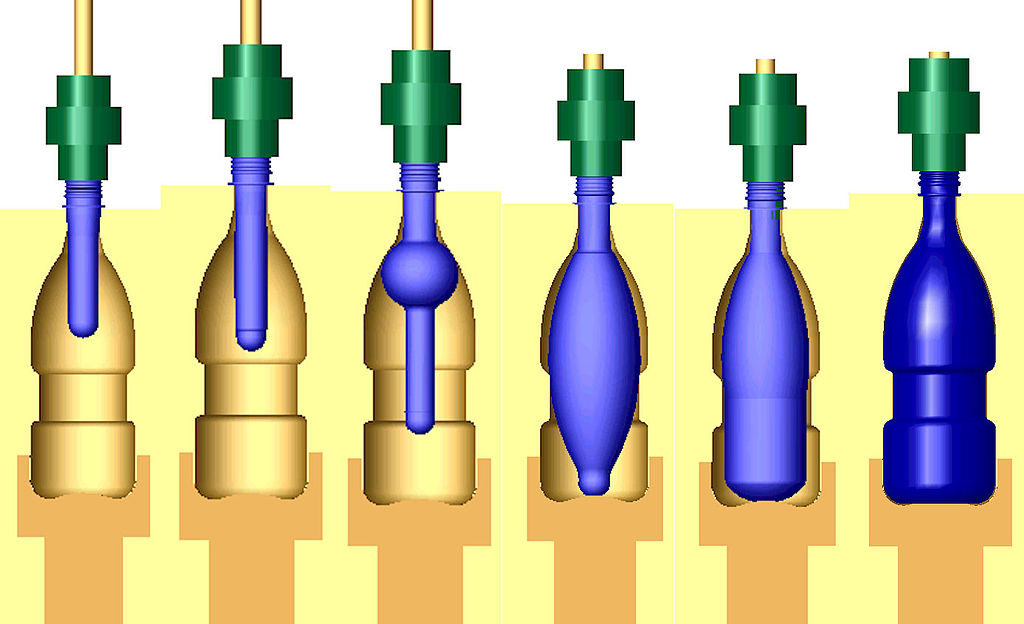
The blow mold is ejected from the core rod after a cooling period and the product is ready.
Advantages of IBM-
- No scrap or extra plastic to trim
- Neck finish and details are of high quality
- Part cost is lowest for high-volume bottles
Disadvantages of IBM-
- Higher tooling cost than extrusion blow molding
- Bottle sizes and shapes can only be made by following an ovality ratio of 2:1 and a blow-up ratio of 3:1
- Barrier strength isn’t increased because the material is not stretched in any axis.
2. Stretch Blow Molding
SBM became popular in the industry after soft drink bottles were introduced. It’s called stretch blow molding because the preform is stretched in the hoop direction and the axial direction before being blown into its final shape. After the preform is made and cooled, it is heated to a specific temperature and closed in the blowing mold.
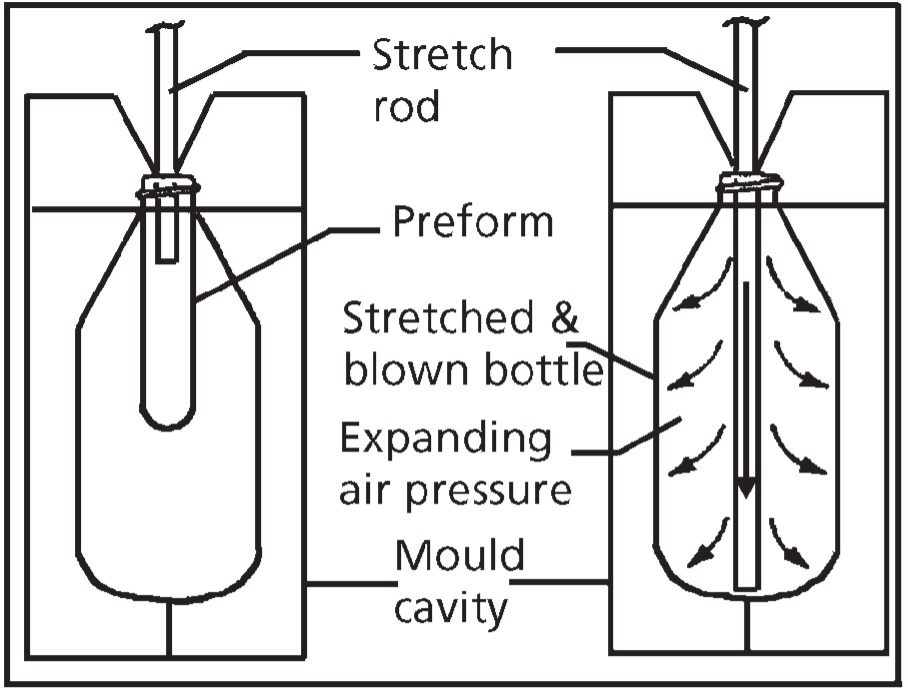
The preform is stretched in the vertical direction with a stretch rod and in the axial direction with air pressure.
Advantages of SBM-
- Can produce products in a variety of sizes and shapes
- Saves money because of the minimal cost of tooling and dies
- A broad range of thermoplastic materials can be used
- Products made in this process have very high tensile strength
Disadvantages of SBM-
- Machinery can be a little bit more expensive than other methods
- It’s not a good profitable option for small runs of production
3. Extrusion Blow Molding
In extrusion blow molding, the thermoplastic material is heated until melting point and extruded into a hollow tube called a parison. The parison is then closed by a cool metal mold. Pressurized air is blown into the parison from one end, inflating it and forcing it into the shape of the metal mold. Lastly, the hollow part is cooled for a sufficient time and ejected from the metal mold.
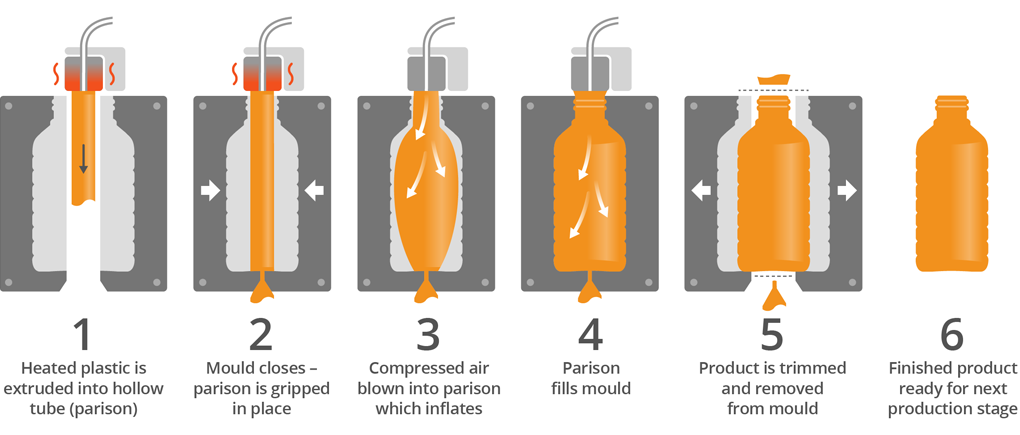
Advantages of extrusion blow molding-
- Tooling and die cost are low
- Production rate is faster than other methods
- Complex parts can be molded efficiently
- Handles can be included in the design
Disadvantages of extrusion blow molding-
- Low barrier strength
- Products are not recyclable because they’re made out of mixed thermoplastic materials
Concluding remarks
There are a lot of parameters to consider when choosing the right molding method for your production business. The most important parameters are: tooling and die cost, Production-rate, machinery cost, material consideration, impact strength, etc.
If you want to know about these processes in more detail or any other topic you’d like us to talk about, feel free to let us know in the comment section below. We would also love to hear your feedback on this article.
Check out some of our other articles down below.





