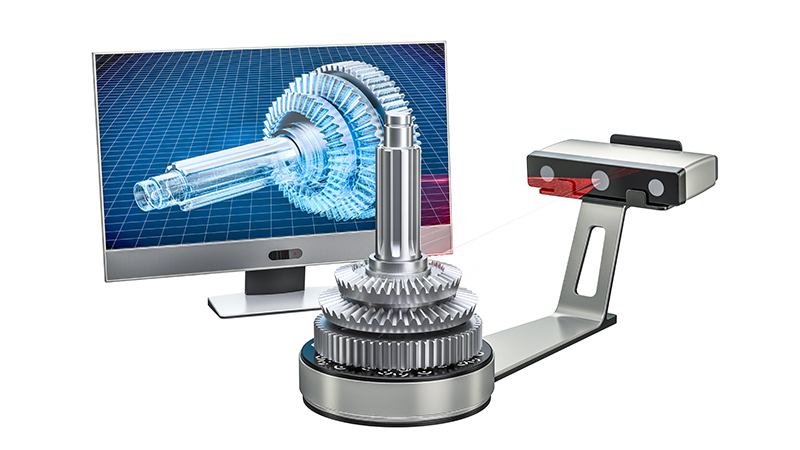
3D scanning technology has become popular in modern times. Its usefulness extends from a doctor looking to make prosthetics to engineers exploring reverse engineering. Not only does it save costs and also time, but it boosts productivity by simplifying the production of new products and services at a quick rate.
Making of high precision 3D models of real-life parts of objects entails using 3D scanning. 3D scan has the capability to cover all the surfaces of an object. Whether you have heard of it or you are new to it, 3D scanning is a powerful tool in the hands of an expert. Industries make most of this technology to achieve great results. Before we delve deeper into this, let us understand some basics concepts about 3D scanning.
What is 3D Scanning Technology?
The 3D scan is the three-dimensional image of an object’s outer surface. 3D models are the compilation of several 3D scans. 3D scan comprises of polygons and also tiny triangles. The triangle and polygon form a polygonal mesh that replicates the geometry of the object up to the minute details.
History of 3D Scanning Technology
3D scanning has been in use since the 20th century. Engineers developed the technology in a bid to accurately replicate various parts of objects. It was mainly used in research and design earlier. The pioneering 3D scanning technology which heralds the beginning of this technology was created in the early 1960s. The earliest scanners mainly utilized cameras, projectors, and also light to complete a scan task. It took a long time to put gather the equipment together which delayed the process. Later on, scanners with the ability to use lasers, shadowing, and also white light to capture and recreate images.
The emergence of computers highlighted the ability of 3D scanning to handle highly complex models and designs. 3D scanning created the possibility of recreating complex surfaces which defied tape measurements in the past. The contact probe was mainly used for complex surfaces but was always slow which was a big limitation. One of the most applicable uses of 3D scanning was in the animation industry to capture humans. Head Scanner from Cyberware Laboratories was in the forefront of this development back in the ’80s. A few years later, a full-body scanner was developed. REPLICA, the first 3D full-body scanner was launched in 1994. It had high body scanning accuracy, high speed, and also detail. Many developments brought color scanning and multidimensional scanning also with high precision accuracy and light speed.

Types of 3D scanning technologies
Four types of 3D scanning technology are currently available. Although two of them are common, the rest are rarely used for specific purposes.
Light-based scanning
This is achieved by projecting light onto an object which then measures and calculates the metrics of the object and recreates it in a digital form. Two types of light-based 3D scanning are available.
The first type of scanning involves beam lasers onto an object. The object deflects the beam of light according to its shape and variations. The scanner measures the deflections and outputs a 3D model of the object. This is similar to 3D printing.
The second type of scanning involves the projection of patterns onto the object. The patterns deform according to the variation on the surface of the object. The scanner measures the deformations and replicates the 3D model of the object.
This is one of the simplest methods. It involves taking several photographs of the objects from different angles and joining them together. The photos can be taken with any good camera while a special 3D scanning software stitches the photos together. The software matches similar pixels with a similar physical point that corresponds and joins them together. This method uses apps like Trnio and Trimensional. This method affords the user the chance to manually input parameters like distortion and focal length. Photogrammetry is very simple and has a high level of accuracy. One major setback of this method is the need for a high-resolution camera. Also, the time it takes the software to scan the images. In the end, it produces good results.
The benefit of 3D Scanning Technology
3D scanning offers several advantages in designing.
Physical objects can be captured quickly and replicated within a short time.
It saves lots of designing time.
It reduces the number of trial times of fitting parts together.
3D scanning helps is the accurate manufacturing of equipment parts
Leading 3D Scanning Technology
3D scanners are cheap contrary to what many believed. 3D scanning solution is far more affordable than the 3D printing solutions. Here are a few of the most affordable 3D scanners in the market now.
Structure Sensor from Occipital, V2 from Matter & Form, Sense 2 from 3D Systems, .0 A from XYZprinting, Eva Lite from Artec 3D, SOL 3D Scanner from Scan Dimension, iReal 2S from ScanTech, SLS Pro S3 from HP, EINSCAN-SE from Shining 3D, and also RangeVision Smart.
You can also check out the best CAD software.
3D Scanning Technology in Manufacturing Industry
3D scanning technology is very useful in industrial design and manufacturing industries. It is applied in all stages of product designing. It accelerates the workflow, saves cost, saves time, and also enhances productivity. Industries may use two or more techniques and scanning technology to achieve optimal quality of designs. Starting from the idea conceptualization to product launch, 3D scanning technology is indispensable in the hands of the engineers.
Future of 3D Scanning Technology
3d scanning is set to shift the paradigm in the nearest future. Not only does it lower manufacturing cost, but it also ensures consistent and top quality products. Thus, industries aim to transform it from mere scanning of objects for replication. Research has shown that 3D scanning technology reduced overall costs in manufacturing by 75%. This is only the beginning, as many more savings will show up. 3D scanning technology is opening doors for archaeological works. Archaeological professionals are utilizing the potentials of 3D scanning in exploring opportunities. Some museums are already using this technology to recreate the fossils and also remains of ancient history. It has increased the learning opportunity for both students and professionals in that field.
Do you have further questions about 3D Scanning?
- How to do 3D Scanning?
- Where to buy 3D Scanners?
- How much 3D Scanners costs?
- How to begin with your first 3D scanning job?
Any other questions or thoughts on your mind concerning 3D scanning technology, drop it in the comment box. Our team will reach out to you in a reasonable time.